Culture
We define culture as the way that members of the organization relate to each other, their work, and the outside world, which distinguishes them from other organizations.
Organizational culture is the invisible force that shapes behavior, decision-making, and overall business performance. When aligned with strategic goals, culture becomes a powerful asset—fueling innovation, engagement, and competitive advantage. A strong culture can unify teams, enhance adaptability, and create a shared sense of purpose, making it easier for organizations to navigate change and achieve lasting success.
However, when culture is misaligned or dysfunctional, it can become a major barrier to growth. Poor communication, resistance to change, lack of trust, and misaligned values can create roadblocks that weaken performance and employee morale. Organizations that fail to recognize and address these dysfunctions often struggle with low engagement, high turnover, and an inability to execute strategy effectively.
By understanding both the functions and dysfunctions of organizational culture, leaders can take proactive steps to reinforce strengths, address weaknesses, and create a thriving work environment that supports long-term success.
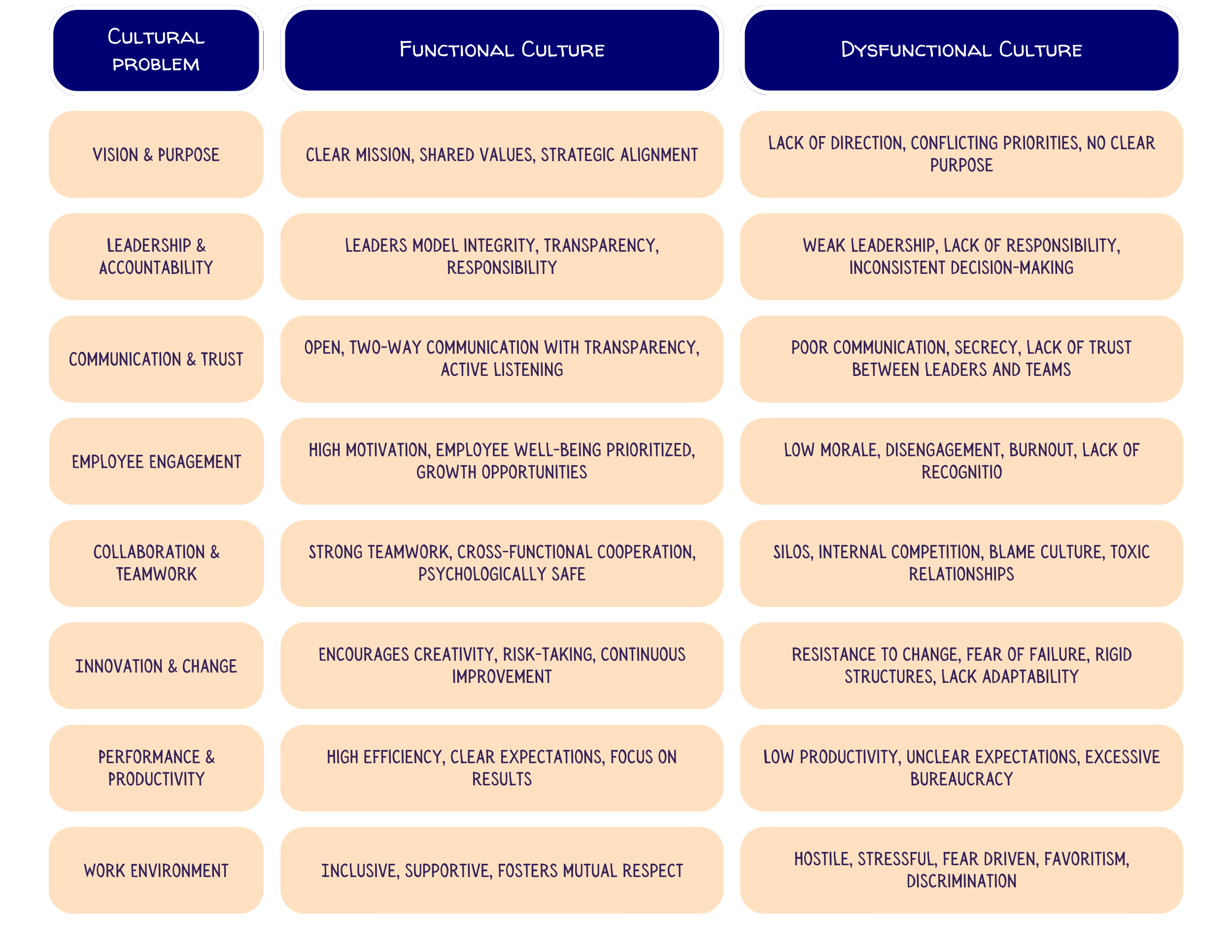
Key Functions of a Strong Organizational Culture
A functional organizational culture serves as the foundation for a high-performing, engaged, and adaptable organization. When culture is aligned with business strategy, it drives growth, innovation, and long-term success. Below are the key functions of a strong culture:
1. Provides a Shared Vision and Purpose
Aligns employees with the organization’s mission, values, and strategic goals.
Creates a sense of belonging and motivation that fosters long-term commitment.
2. Enhances Employee Engagement and Retention
Builds a positive work environment that supports employee well-being.
Encourages open communication, trust, and collaboration.
Reduces turnover by ensuring employees feel valued and connected.
3. Drives Innovation and Adaptability
Encourages creative problem-solving and risk-taking.
Helps organizations respond quickly to market changes and disruptions.
Fosters a growth mindset, where employees continuously learn and evolve.
4. Strengthens Organizational Performance and Productivity
Creates clear expectations, accountability, and decision-making processes.
Reduces inefficiencies by aligning work practices with strategic priorities.
Encourages teamwork, cross-functional collaboration, and knowledge-sharing.
5. Builds a Trust-Based Leadership and Communication Framework
Establishes transparent leadership that promotes integrity and accountability.
Encourages a speak-up culture, where employees feel safe sharing ideas and concerns.
Fosters consistent messaging, reducing confusion and workplace conflict.
6. Reinforces Organizational Identity and Brand Reputation
Strengthens the company’s brand by reflecting its core values.
Enhances customer relationships by ensuring consistent and ethical business practices.
Differentiates the organization in the marketplace as an employer of choice.
7. Facilitates Change and Long-Term Sustainability
Supports a culture of learning, resilience, and continuous improvement.
Ensures that employees and leaders are aligned and committed to transformation.
Helps organizations navigate mergers, expansions, and leadership transitions smoothly.
A functional culture doesn’t happen by chance—it requires intentional effort, continuous assessment, and strategic alignment. Organizations that actively shape and reinforce their culture set themselves up for sustainable success.
Common Dysfunctions of Organizational Culture
When organizational culture becomes misaligned or dysfunctional, it can undermine engagement, innovation, and performance, creating barriers to success. Below are the most common cultural dysfunctions that can weaken an organization and hinder growth:
1. Lack of Clear Vision and Alignment
Employees are uncertain about the organization’s mission, values, and goals.
Leadership lacks consistent direction, leading to confusion and disengagement.
Departments and teams operate in silos, with little collaboration or shared purpose.
📉 Impact: Employees feel disconnected, leading to reduced motivation and productivity.
2. Poor Communication and Lack of Transparency
Leaders fail to share critical information, leaving employees in the dark.
Communication is one-way, with little opportunity for employee feedback.
Important messages are inconsistent or unclear, causing misunderstandings.
📉 Impact: Mistrust grows, teamwork suffers, and decision-making slows down.
3. Resistance to Change and Innovation
Employees and leaders are fearful of risk, leading to stagnation.
Bureaucracy and rigid structures make adapting to market shifts difficult.
New ideas are ignored, dismissed, or met with skepticism.
📉 Impact: The organization struggles to innovate, losing its competitive edge.
4. Toxic Work Environment and Lack of Psychological Safety
Employees fear speaking up due to blame, criticism, or retaliation.
Unhealthy competition and office politics create a stressful workplace.
Cliques and favoritism lead to exclusion and disengagement.
📉 Impact: High turnover, burnout, and a decline in team collaboration.
5. Weak Leadership and Lack of Accountability
Leaders fail to set clear expectations and model desired behaviors.
No accountability for poor performance, leading to frustration among employees.
Leadership avoids difficult conversations, allowing dysfunctions to persist.
📉 Impact: Employees lose confidence in leadership, leading to disengagement.
6. Low Employee Engagement and Morale
Employees feel undervalued, unrecognized, or overworked.
There’s no investment in professional development or growth opportunities.
Work culture prioritizes results over well-being, leading to burnout.
📉 Impact: Productivity declines, and talent retention becomes a challenge.
7. Mismatched Cultural Identity and Strategy
The actual culture does not support the business strategy or market demands.
Leadership says one thing but does another, leading to credibility gaps.
Cultural values are not reinforced in hiring, training, or decision-making.
📉 Impact: Strategic goals are difficult to achieve, and employee trust erodes.
Overcoming Cultural Dysfunctions
Dysfunctional cultures don’t fix themselves—they require intentional leadership and strategic cultural transformation. By identifying and addressing these dysfunctions, organizations can create a thriving, engaged, and high-performing workplace that drives long-term success.
Need to diagnose your culture and build a stronger foundation? Contact Dynamic Perspectives today to take the next step in cultural transformation!